Graph Algorithms Part I.
MST 最小生成树
public class MST extends Tree {
private double totalWeight; // Total weight of all edges in the tree
public MST(int root, int[] parent, List<Integer> searchOrder,
double totalWeight) {
super(root, parent, searchOrder);
this.totalWeight = totalWeight;
}
public double getTotalWeight() {
return totalWeight;
}
}
ShortestPathTree类
public class ShortestPathTree extends Tree{
private double[] cost;
public ShortestPathTree(int source , int[] parent , List<Integer> searchOrder , double[] cost){
super(source , parent , searchOrder);
this.cost = cost;
}
public double[] getCost() {
return cost;
}
public void printAllPaths(){
System.out.println("All shortest paths from " + vertices.get(getRoot()) + " are:");
for (int i = 0; i < cost.length; i++) {
printPath(i);
System.out.println("(cost: " + cost[i] +")");
}
}
}
1.Prim 最小生成树 , 即最小的总权重的生成树
public MST getMinSpanningTree(){
return getMinSpanningTree(0);
}
//包括了连通图里的所有顶点,
//且其所有边的权值之和亦为最小
//连通图足够密集时(当E满足Ω(VlogV)条件时),
//可较显著地提高运行速度。
//搜索到哪个edge权重最小就加入到T
public MST getMinSpanningTree(int sourceVertex) {//Algorithm Prim
double[] cost = new double[size()];
// cost[v] stores the cost by adding v to the tree
Arrays.fill(cost, Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY);
cost[sourceVertex] = 0;
int[] parent = new int[size()];
parent[sourceVertex] = -1;
double totalWeight = 0;
List<Integer> T = new ArrayList<>();
//boolean[] isTnT = new boolean[size()];
while (T.size() < size()){
int u = -1 ;
double curMinCost = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) {
if (!T.contains(i) && cost[i] < curMinCost){
//我们可以用一个boolean数组来代替contains方法 : !isTnT[i]
//从而优化时间复杂度
//开始寻找最小值权重edge
curMinCost = cost[i];
u = i;
}
}
// if (u == -1) break; else T.add(u);
//Add a new vertex to T
T.add(u);
totalWeight += cost[u];//累加最小权重
//isTnT[u] = true;
for (Edge e:neighbors.get(u)){
if (!T.contains(e.v) && cost[e.v] > ((MyWeightedEdge)e).weight){//adjust cost[v]
//对每个edge的权重进行比较,找出最小值
cost[e.v] = ((MyWeightedEdge)e).weight;
parent[e.v] = u;
}
}
}
return new MST(sourceVertex , parent , T , totalWeight);
//返回一个MST
}
}
2.Kruskal 另一种寻找最小生成树算法
重复寻找最小总权重edge,若不出现环,则添加到树
用了PriorityQueue去实现
public MST getMinimumSpanningTree() {
WeightedGraph<V> t = new WeightedGraph<>();
for (int i = 0; i < this.getSize(); i++) {
t.addVertex(this.vertices.get(i));
}
PriorityQueue<WeightedEdge> edgeList = getEdges();
double totalWeight = 0;
while (!edgeList.isEmpty()) {
WeightedEdge e = edgeList.remove();
t.neighbors.get(e.u).add(new WeightedEdge(e.u, e.v, e.weight));
t.neighbors.get(e.v).add(new WeightedEdge(e.v, e.u, e.weight));
if (t.getACycle() != null) {
t.neighbors.get(e.u).remove(t.neighbors.get(e.u).size() - 1);
t.neighbors.get(e.v).remove(t.neighbors.get(e.v).size() - 1);
} else {
totalWeight += e.weight;
}
}
Tree tree = t.dfs(0);
int[] parent = new int[vertices.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < parent.length; i++) {
parent[i] = tree.getParent(i);
}
return new MST(tree.getRoot(), parent, tree.getSearchOrder(), totalWeight);
}
public PriorityQueue<WeightedEdge> getEdges() {
PriorityQueue<WeightedEdge> list = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < this.getSize(); i++) {
for (Edge e : this.neighbors.get(i)) {
if (e.u < e.v) {
list.add((WeightedEdge) e);
}
}
}
return list;
}
public List<Integer> getACycle() {
List<Integer> allVertices = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < this.vertices.size(); i++) {
allVertices.add(i);
}
List<List<Edge>> neighbors = cloneEdges();
List<Integer> searchOrder = new ArrayList<>();
int[] parent = new int[vertices.size()];
// Initialize parent[i] to -1
Arrays.fill(parent, -1);
// Mark visited vertices
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[vertices.size()];
while (allVertices.size() > 0) {
int v = allVertices.get(0);
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(v);
searchOrder.add(v);
allVertices.remove(new Integer(v));
isVisited[v] = true; // Vertex x visited
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int x = stack.peek();
if (neighbors.get(x).size() == 0) {
stack.pop();
} else {
// Find the next unvisited neighbor of x
for (int i = neighbors.get(x).size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
Edge e = neighbors.get(x).get(i);
if (!isVisited[e.v]) {
parent[e.v] = x; // The parent of vertex e.v is x
stack.push(e.v); // Add a new neighbor to the stack
isVisited[e.v] = true; // Vertex x visited
searchOrder.add(e.v);
allVertices.remove(new Integer(e.v));
neighbors.get(x).remove(i);
break;
} else if (e.v != parent[x]) {
// A path is found
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(e.v);
while (x != e.v) {
list.add(x);
x = parent[x];
}
return list;
} else {
neighbors.get(x).remove(i);
}
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
public List<List<Edge>> cloneEdges() {
List<List<Edge>> neigborCopy = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<Edge> neighbor : neighbors) {
List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<>();
for (Edge e : neighbor) {
edges.add(e);
}
neigborCopy.add(edges);
}
return neigborCopy;
}
Union-Find并查集 实现Kruskal
/**
* @author Minezeratul
*/
public class KruskalUF {
private Queue<WeightedEdge> mst;
double weight;
public KruskalUF(WeightedGraph G) {
mst = new LinkedList<>();
PriorityQueue<WeightedEdge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((Comparator.comparingDouble(o -> o.weight)));
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(G.getSize());
for (int i = 0; i < G.getSize(); i++) {//add all edges
for (int j = 0; j < G.getNeighbor(i).size(); j++) {
pq.offer((WeightedEdge) G.getNeighbor(i).get(j));
}
}
while (!pq.isEmpty() && mst.size() < G.getSize() - 1) {
WeightedEdge e = pq.poll();
int v = e.u, w = e.v;
if (uf.connected(v, w)) {
continue;
}
uf.union(v, w);
mst.offer(e);
weight += e.weight;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "" + mst;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] vertices = {"0", "1", "2", "3", "4"};
int[][] edges = {
{0, 1, 2}, {0, 3, 8},
{1, 0, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {1, 3, 3},
{2, 1, 7}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5},
{3, 0, 8}, {3, 1, 3}, {3, 2, 4}, {3, 4, 6},
{4, 2, 5}, {4, 3, 6}
};
WeightedGraph<String> graph = new WeightedGraph<>(vertices, edges);
graph.getMinimumSpanningTree().printTree();
System.out.println(graph.getMinimumSpanningTree().getTotalWeight());
KruskalUF k = new KruskalUF(graph);
System.out.println(k.weight);
System.out.println(k);
}
}
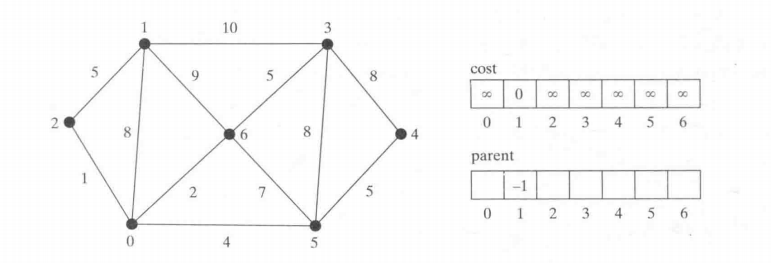
3.Dijkstra 单源最短路径 ,即最小总权重的路径
//要求图中不存在负权边
//每次遍历到始点距离最近且未访问过的顶点的邻接节点,直到扩展到终点为止
//寻找点到点之间的最小总权重路线
public ShortestPathTree getShortestPath(int sourceVertex){//Algorithm Dijkstra
double[] cost = new double[size()];
Arrays.fill(cost , Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY);
cost[sourceVertex] = 0 ;
int[] parent = new int[size()];
parent[sourceVertex] = -1;
List<Integer> T = new ArrayList<>();
while (T.size() < size()){
int u = -1;
double curMinCost = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) {
//开始搜寻加权图
if (!T.contains(i) && cost[i] < curMinCost){
curMinCost = cost[i];
u = i;
}
}
T.add(u);
for (Edge e:neighbors.get(u)) {
//与Prim的不同之处
if (!T.contains(e.v) && cost[e.v] > cost[u] + ((MyWeightedEdge)e).weight){
cost[e.v] = cost[u] + ((MyWeightedEdge)e).weight;
parent[e.v] = u;
}
}
}
return new ShortestPathTree(sourceVertex , parent , T , cost);
}
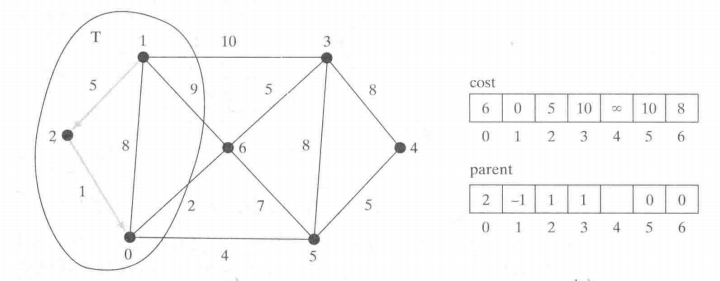
如图所示,我们从1开始 , 然后就到2(min cost) ,更新cost和parent ;然后从2去到0 , 更新 , 从 0 去到 6 ;
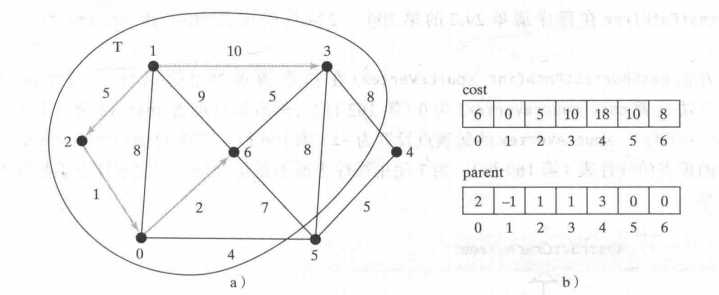
3和5的权重相同,我们先去到3,此时更新cost,cost[4]变成了18 , 因为我们还没有搜寻到{5, 4 , 4}
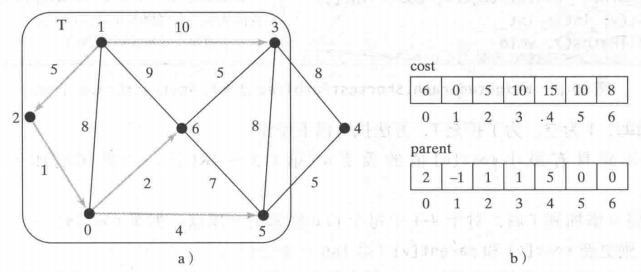
此时添加5 , cost[4]才更新成最小总权重15